 |
Indotco InternationalIt's a personal service. |
|
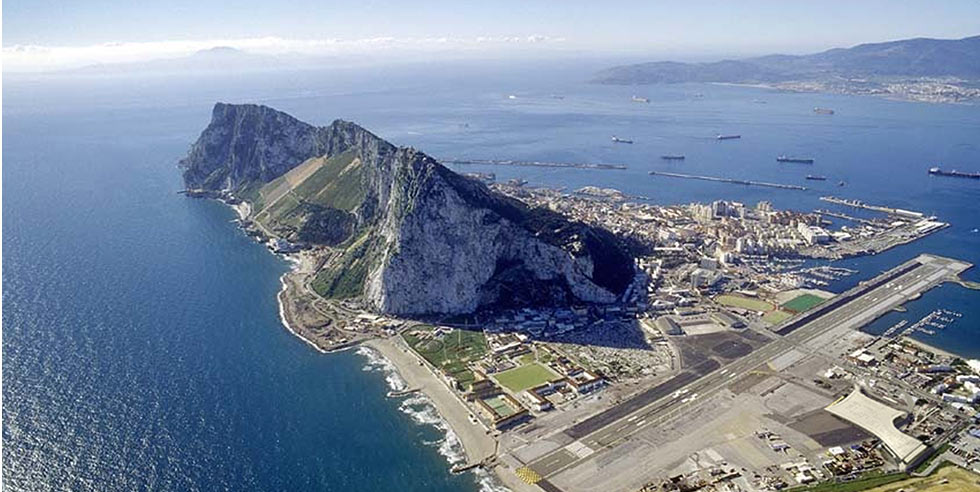

About Gibraltar - History, Politics and Economy
Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, bordered by Spain to the north. Here are some key points about Gibraltar:
Geography and Landmarks Gibraltar is located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, at the western entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. The territory consists mainly of the Rock of Gibraltar, a massive limestone ridge rising up to 426 meters (1,398 feet) above sea level. The rock itself is iconic and visible from afar, often shrouded in mist and home to a network of tunnels and caves. History Gibraltar's history is rich and complex: - Ancient Times: The Rock has been inhabited since ancient times, with evidence of settlement dating back to the Neanderthals. - Medieval Period: It became a strategic military post during the Middle Ages, controlled by various powers including the Moors and later Spain. - British Rule: In 1704, during the War of the Spanish Succession, an Anglo-Dutch force captured Gibraltar. The territory was formally ceded to Britain by Spain in 1713 under the Treaty of Utrecht, and it has remained under British sovereignty since then. Government and Politics Gibraltar is a British Overseas Territory with a high degree of self-government. It has its own parliament (the Gibraltar Parliament) and legal system. The UK is responsible for defense and foreign affairs, though Gibraltar is largely autonomous in domestic matters. Economy Gibraltar has a thriving economy driven by several key sectors: - Financial Services: It is a significant offshore financial center with a well-regulated banking sector and favorable tax regime. - Tourism: The territory attracts tourists drawn to its historical sites, duty-free shopping, and the natural beauty of the Rock. - Shipping and Port Services: Gibraltar has a busy port and is a refueling and bunkering hub for maritime traffic passing through the Strait. Culture and Society Gibraltar's population is diverse and multicultural: - Demographics: The majority are Gibraltarians of mixed Genoese, Maltese, British, and Spanish descent. There are also significant communities of British expatriates and other nationalities. - Languages: English is the official language, but Spanish is widely spoken. A unique local dialect, Llanito, blends English with Andalusian Spanish and influences from other languages. Strategic Importance Strategically, Gibraltar is crucial due to its control over the Strait of Gibraltar, one of the busiest shipping lanes globally. It provides a gateway between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, making it historically significant for naval and commercial purposes. Wildlife and Environment Gibraltar is home to the famous Barbary macaques, the only wild monkey population in Europe. The Gibraltar Nature Reserve encompasses much of the Upper Rock area and is a protected area for its rich biodiversity and unique geological formations. Challenges and Issues Gibraltar faces challenges such as disputes with Spain over sovereignty and border controls. However, its strong economy and strategic location continue to ensure its prominence on the global stage. In summary, Gibraltar blends its historical significance with a modern economy and vibrant culture, making it a unique and intriguing territory at the crossroads of Europe and Africa. Border issues have been a significant aspect of Gibraltar's history and continue to influence its relations with neighboring Spain. Here are the key points regarding border issues: Historical Context 1. Treaty of Utrecht (1713): Under this treaty, Gibraltar was ceded to Britain by Spain "in perpetuity." However, Spain has periodically sought to regain sovereignty over Gibraltar. 2. Closed Border Period (1969-1985): During the regime of Francisco Franco in Spain, the border between Gibraltar and Spain was closed. This period severely restricted movement and trade between Gibraltar and the neighboring Spanish region of Andalusia. Current Border Situation 1. Open Border: Since the reopening of the border in 1985, there has been free movement of people between Gibraltar and Spain. Thousands of people cross the border daily for work, tourism, and other purposes. 2. Checks and Controls: Despite the open border, there are occasional tensions over border controls. Both Gibraltar and Spain maintain border checkpoints where identity and vehicle checks are conducted, sometimes leading to delays and occasional disputes. 3. Sovereignty Dispute: Spain continues to assert its claim of sovereignty over Gibraltar and often uses border issues as a means to apply pressure. Gibraltar, however, maintains its stance of self-determination and remains under British sovereignty. 4. European Union Influence: While Gibraltar is not part of the Schengen Area, its border with Spain became significant during the Brexit negotiations. Gibraltar, being a British Overseas Territory, was not part of the EU, but its border with Spain created complexities regarding movement of people and goods post-Brexit. Impact on Daily Life 1. Economic Impact: The fluidity of the border is crucial for Gibraltar's economy, especially for tourism and cross-border workers who contribute significantly to Gibraltar's workforce. 2. Political Sensitivities: Border issues are often politicized, affecting diplomatic relations between Gibraltar, the UK, and Spain. The issues surrounding sovereignty and border controls remain sensitive topics for all parties involved. Future Prospects 1. Negotiations: Efforts have been made to improve relations and reduce tensions, including through bilateral talks between Gibraltar, the UK, and Spain. However, reaching a lasting agreement on sovereignty and border issues remains challenging. 2. International Support: Gibraltar enjoys strong support from the UK government and has received assurances regarding its sovereignty. The international community generally recognizes Gibraltar's right to self-determination, but the issue remains unresolved. In conclusion, while the border between Gibraltar and Spain is currently open and facilitates movement, it remains a focal point for political tensions and diplomatic discussions surrounding sovereignty and territorial integrity. Brexit has had significant implications for Gibraltar, given its unique geopolitical and economic situation. Here are the key impacts of Brexit on Gibraltar: Border and Movement 1. Schengen Area Exclusion: Gibraltar is not part of the Schengen Area, unlike Spain, which has created challenges for movement of people and goods across the border. Post-Brexit, border checks have become more stringent, impacting daily commuters and businesses that rely on cross-border trade. 2. Customs and Trade: Gibraltar has been affected by changes in customs procedures and tariffs due to Brexit. There have been efforts to streamline these processes to minimize disruptions, but businesses have faced new administrative burdens. Economic Factors 1. Financial Services: Gibraltar is a significant financial hub, particularly in insurance and online gaming sectors. Brexit has raised concerns about access to the EU market and passporting rights, which allowed firms based in Gibraltar to operate across the EU. 2. Tourism and Services: Gibraltar's tourism sector, which is vital to its economy, has faced uncertainties post-Brexit regarding travel arrangements and visitor numbers, although efforts have been made to mitigate these impacts. Political and Sovereignty Issues 1. Sovereignty: Brexit renewed discussions about Gibraltar's sovereignty, with Spain seeking to influence negotiations. Gibraltar's status as a British Overseas Territory means its relationship with the EU was tied to the UK's negotiations, impacting its autonomy and international standing. 2. Negotiations and Agreements: Gibraltar negotiated separately from the UK with the EU to ensure its interests were represented. The Gibraltar Protocol was included in the UK-EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement to address specific issues such as movement of people and goods. Social and Cultural Dynamics 1. Residency and Rights: There have been concerns among residents of Gibraltar, particularly those who hold dual British and EU citizenship, about their rights post-Brexit. Efforts have been made to clarify residency requirements and protect rights where possible. 2. Identity and Integration: Brexit has prompted discussions about Gibraltar's identity and its integration within the broader European context, as it navigates its relationship with both the UK and the EU. Future Outlook 1. Adaptation and Resilience: Gibraltar has shown resilience in adapting to post-Brexit realities, including diversifying its economy and strengthening ties with international partners beyond the EU. 2. Negotiations and Diplomacy: Continued negotiations between Gibraltar, the UK, Spain, and the EU will be crucial in shaping its future relationship, ensuring economic stability, and safeguarding its unique status. In summary, Brexit has posed both challenges and opportunities for Gibraltar, impacting its economy, politics, and social fabric. The territory continues to navigate its post-Brexit relationship with the UK, Spain, and the wider European Union, seeking to protect its interests while maintaining stability and prosperity. You have some more questions? Contact us for a free quote. |